Testing Guide
The Todos application includes a comprehensive testing strategy covering all aspects from unit tests to performance benchmarks. Our testing pyramid ensures high code quality and confidence in deployments.
Testing Strategy
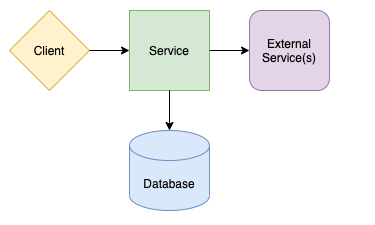
The application follows a multi-layered testing approach:
- Unit Tests - Fast, isolated tests for business logic
- Integration Tests - Component interaction testing
- Acceptance Tests - End-to-end behavior validation
- Performance Tests - Load testing and performance validation
Running Tests
Quick Test Commands
# Run all unit tests
./mvnw test
# Run all tests including integration
./mvnw verify
# Run specific module tests
./mvnw test -pl domain
./mvnw test -pl application
# Run with coverage report
./mvnw clean verify jacoco:report
Performance Testing
# Run Gatling performance tests
./mvnw -pl performance-benchmark verify
# Run performance tests standalone
./mvnw -pl performance-benchmark gatling:test
Unit Testing

Coverage: 100% line coverage with mutation testing
Technologies:
- JUnit 5 for test framework
- Mockito for mocking dependencies
- AssertJ for fluent assertions
- EqualsVerifier for equals/hashCode contracts
Test Structure:
domain/src/test/java/
├── ChecklistTest.java # Domain entity tests
├── ChecklistIdTest.java # Value object tests
├── ChecklistNameTest.java # Value object tests
└── TodoTest.java # Domain logic tests
Example Unit Test:
@Test
void shouldCreateChecklistWithName() {
// Given
ChecklistName name = ChecklistName.newChecklistName("Shopping List");
// When
Checklist checklist = Checklist.namedEmptyChecklist(name.getValue());
// Then
assertThat(checklist.getName()).isEqualTo(name);
assertThat(checklist.getTodos()).isEmpty();
}
Quality Gates:
- 100% line coverage required
- 100% mutation score with PIT testing
- All equals/hashCode contracts verified
Integration Testing
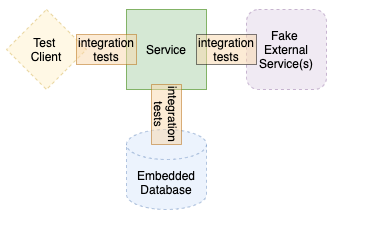
Coverage: Full API endpoint coverage with WebFlux testing
Technologies:
- Spring Boot Test with WebFlux
- TestContainers for database integration
- WebTestClient for reactive web testing
- HAL+JSON assertion helpers
Test Structure:
application/src/test/java/
├── ChecklistsResourceIT.java # Checklists API tests
├── ChecklistResourceIT.java # Individual checklist API tests
├── TasksResourceIT.java # Tasks API tests
└── RootResourceIT.java # Root API discovery tests
Example Integration Test:
@WebFluxTest(controllers = ChecklistsResource.class)
class ChecklistsResourceIT {
@Autowired
private WebTestClient webTestClient;
@MockBean
private CreateChecklistUseCase createChecklistUseCase;
@Test
void shouldCreateChecklist() {
// Given
when(createChecklistUseCase.createChecklist(any()))
.thenReturn(Mono.just(namedEmptyChecklist("Shopping List")));
// When & Then
webTestClient
.post()
.uri("/checklists")
.contentType(APPLICATION_JSON)
.accept(HAL_JSON)
.bodyValue("{\"name\": \"Shopping List\"}")
.exchange()
.expectStatus().isCreated()
.expectHeader().exists("Location")
.expectBody()
.jsonPath("$.name").isEqualTo("Shopping List")
.jsonPath("$._links.self.href").exists();
}
}
Acceptance Testing
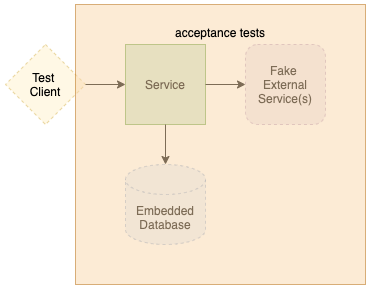
Coverage: Complete user journey validation
Technologies:
- Cucumber for BDD scenarios
- Spring Boot integration testing
- Docker Compose for full stack testing
- REST Assured for API testing
Test Structure:
acceptance-tests/src/test/
├── resources/features/ # Cucumber feature files
├── java/steps/ # Step definitions
└── java/support/ # Test configuration
Example Feature:
Feature: Checklist Management
As a user
I want to manage checklists
So that I can organize my todos
Scenario: Creating a new checklist
Given the API is available
When I create a checklist named "Weekend Tasks"
Then the checklist should be created successfully
And the response should include a self link
And the checklist should be retrievable by ID
Running Acceptance Tests:
# Start the application stack
docker-compose -f config/docker-compose.yml up -d
# Run acceptance tests
./mvnw -pl acceptance-tests verify
# View cucumber reports
open acceptance-tests/target/cucumber-reports/index.html
Performance Testing
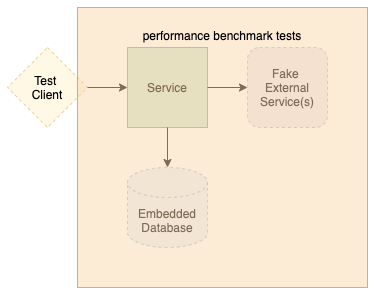
Load Testing with Gatling (Java SDK)
Performance Goals:
- Response time: 95th percentile < 250ms
- Response time: 99th percentile < 900ms
- Success rate: 100%
- Throughput: 30+ requests/second
Test Structure:
performance-benchmark/src/test/java/
├── BenchmarkSimulation.java # Main performance test
├── RootResourceAction.java # API discovery actions
├── ChecklistsResourceAction.java # Checklist creation actions
├── ChecklistResourceAction.java # Checklist retrieval actions
└── HealthCheckAction.java # Health check actions
Current Performance Results:
- 5,487 total requests processed
- Mean response time: 2ms
- 95th percentile: 5ms
- 99th percentile: 8ms
- Success rate: 100%
- Throughput: 91.45 requests/second
Running Performance Tests:
# Run full performance suite
./mvnw -pl performance-benchmark verify
# Run specific performance test
./mvnw -pl performance-benchmark gatling:test \
-Dgatling.simulationClass=BenchmarkSimulation
# View performance report
open performance-benchmark/target/gatling/*/index.html
Performance Test Scenarios:
- Health Check Journey: Continuous health monitoring (1 RPS)
- Core API Journey: Full checklist lifecycle (30 RPS)
- Discover API endpoints
- Create new checklist
- Retrieve created checklist
Code Quality Metrics
Static Analysis Tools:
- Checkstyle: Code formatting and style consistency
- SpotBugs: Static analysis for common bugs and issues
- PMD: Code quality rules and best practices
- ErrorProne: Google’s bug pattern detector
Coverage & Testing Quality:
- JaCoCo: Line and branch coverage measurement
- PIT: Mutation testing for test quality assessment
Security Scanning:
- FindSecBugs: Security vulnerability pattern detection
- Dependency validation: Automated dependency updates
Continuous Integration
GitHub Actions Pipeline:
- Build: ./mvnw clean compile
- Unit Tests: ./mvnw test
- Integration Tests: ./mvnw verify
- Performance Tests: ./mvnw -pl performance-benchmark verify
- Quality Gates: All quality checks must pass
- Security Scan: FindSecBugs vulnerability detection
- Docker Build: Native image compilation
Quality Gates:
- All tests must pass (0 failures)
- Code coverage ≥ 80%
- No critical security vulnerabilities
- Performance benchmarks within SLA
- All static analysis checks pass
Test Data Management
Test Isolation:
- Each test uses unique identifiers (UUID)
- Database state isolated per test
- No shared state between tests
- Clean setup/teardown procedures
Mock Strategy:
- Repository layer mocked for unit tests
- Real database for integration tests
- TestContainers for isolated database testing
- External service mocks for acceptance tests
Best Practices
- Fast Feedback: Unit tests run in milliseconds
- Test Pyramid: More unit tests, fewer integration tests
- BDD Scenarios: Business-readable acceptance criteria
- Performance Baseline: Automated performance regression detection
- Test Documentation: Self-documenting test names and scenarios
For more details on specific testing approaches, see individual test modules in the codebase.